When we think about medicines, we often focus on how they help us feel better. But did you know that the way a medicine is made can affect its effectiveness?
Two important methods to help medicines work better are enteric coating and film coating. Both methods coat tablets to protect them and control how they release the medicine.
Let’s explore these pharmaceutical coatings, how they can affect your medication, and which one might be best for you.

Ready to enhance your production with high-quality coating machines?
Enteric coating and film coating are two popular methods used in the pharmaceutical industry. Both processes are designed to enhance the effectiveness of medicines by protecting the ingredients and ensuring that they are delivered to the right part of the digestive system.
While they serve similar purposes, they have different applications and characteristics.

What is enteric coating? Enteric coating is a special layer that is put on some tablets. This coating helps protect the medicine inside from stomach acid.
The coating is made to dissolve in the intestine instead of the stomach. This is important because some medicines can be damaged by stomach acid, and enteric coating helps keep them safe.
The enteric coating is usually made from special materials that resist the acidic environment of the stomach. This ensures that the medicine remains intact until it reaches the intestine, where it can be absorbed properly.
It is important not to break enteric-coated tablets. When you break them, you can damage the coating. This means the medicine might dissolve in the stomach instead of the intestine. If that happens, the medicine might not work as it should, and you could get stomach upset.
For example, if you have an enteric-coated tablet that is meant to relieve heartburn, breaking it can lead to stomach irritation instead of allowing it to work effectively in the intestines.
No, it’s not a good idea to crush enteric-coated tablets. Crushing them will break the coating. This can change how the medicine works. Always check with a doctor or pharmacist if you need help with taking your medicine.
Some people might think that crushing a tablet can make it easier to swallow, but it can lead to unintended consequences. If you need to take an enteric-coated tablet, try to find alternative methods, like swallowing the tablet whole or asking for a liquid version if available.

What is film coating? Film coating is another way to protect tablets. It involves applying a thin layer over the tablet. This layer can help make the tablet easier to swallow.
The film coating can also protect the medicine from moisture and light. Unlike enteric coating, film coating usually dissolves in the stomach. This means that the medicine can start to work quickly.
Film coatings are typically made from polymers that dissolve readily in the gastrointestinal tract. This means that as soon as the tablet enters the stomach, the coating breaks down, allowing the medicine to be released and absorbed into the bloodstream.
Film-coated tablets are often more appealing to patients because they tend to have a smoother surface. This makes them easier to swallow. The film coating can also be flavored, which can help mask any unpleasant taste from the ingredients inside.
In addition to improving palatability, film coating provides a protective barrier that prevents moisture and light from degrading the tablet. This makes film-coated tablets a great choice for many types of medications that need to maintain their effectiveness over time.
Let’s look at some key differences between enteric coating and film coating:
| Feature/Characteristic | Enteric Coating | Film Coating |
| Purpose and Function | Protects from stomach acid; releases in the intestine | Enhances swallowability; protects from moisture |
| Dissolution Location | Dissolves in the intestine | Dissolves in the stomach |
| Material Composition | Made from acid-resistant polymers | Made from polymers that dissolve easily |
| Application Type | Used for medications sensitive to stomach acid | Used for various medications |
| Cost and Production Complexity | Generally more expensive and complex | Typically less expensive and easier to apply |
| Ability to Control Drug Release | Allows controlled release in the intestine | Primarily designed for immediate release |
Enteric coating protects the medicine from stomach acid and allows it to dissolve in the intestine. Film coating helps make tablets easier to swallow and protects them from moisture. Each coating serves a unique function based on the specific needs of the medicine.
Enteric-coated tablets dissolve in the intestine. Film-coated tablets dissolve in the stomach. This is important for how and when the medicine is released in the body. For example, if a medicine needs to be absorbed in the intestine for maximum effectiveness, enteric coating is essential.
Enteric coatings are often made from materials that resist stomach acid, such as polymers. Film coatings are usually made from materials that dissolve easily in the stomach. The choice of materials impacts how the tablet behaves once ingested.
Enteric coating is used for medicines that need to avoid stomach acid. Film coating can be used for many types of tablets, especially those that are difficult to swallow. This versatility makes film coating a popular choice in the pharmaceutical industry.
Enteric coating can be more expensive and complex to apply compared to film coating. This is because the materials and processes involved in enteric coating require careful handling. Manufacturers may need specialized equipment and techniques to ensure proper coating.
Enteric coating allows for controlled release of the medicine in the intestine. The film coating can also help control the release but is mainly designed for protection and ease of swallowing. Understanding how each coating impacts drug release is key for manufacturers and healthcare providers.
When deciding between enteric coating and film coating, consider these important factors:
| Factor | Enteric Coating | Film Coating |
| Correct Administration | Should not be broken or crushed | Can be chewed or crushed (depending on instructions) |
| Avoiding Side Effects | Protects against stomach irritation | May not protect against stomach acid |
| Medication Interactions | Helps reduce stomach irritation with other medications | May not provide protection against interactions |
| Medication Safety | Safe for drugs that irritate the stomach | Generally safe, but may not offer specific protection |
Make sure to follow the instructions for taking the medicine. Some tablets need to stay whole, while others can be chewed or crushed. For example, enteric-coated tablets should not be broken or crushed. This ensures they will work as intended.
Choosing the right coating can help prevent side effects. Some medicines might cause stomach upset if they are not coated properly. For example, an enteric coating can help protect sensitive medications from the harsh environment of the stomach.
This is particularly important for drugs that are known to irritate the stomach lining. If these drugs are not enteric-coated, they could lead to discomfort and reduce patient compliance.
Some medications can interact negatively with others. The choice of coating can help manage these interactions. For example, enteric-coated medicines may be a better choice for patients taking other medications that could cause stomach irritation.
This can lead to a better overall treatment experience and improve the effectiveness of the medications being used. Discussing potential interactions with a healthcare provider can help determine the best coating for specific situations.
It is important to ensure that the coating is safe for the intended use. Both enteric and film coatings are generally safe, but you should always consult with a healthcare provider if you have concerns. Understanding the implications of the coating on drug safety can help you make informed decisions.
For example, some patients may have allergies to specific materials used in coatings. Being aware of this can help avoid potential adverse reactions and ensure that the patient is safe while taking their medications.
If you are looking for high-quality coating solutions, consider Canaan’s coating machines.
We offer reliable and efficient options for both enteric and film coating processes. These machines help ensure that medicines are coated properly, enhancing their effectiveness.
Contact us today to learn more!
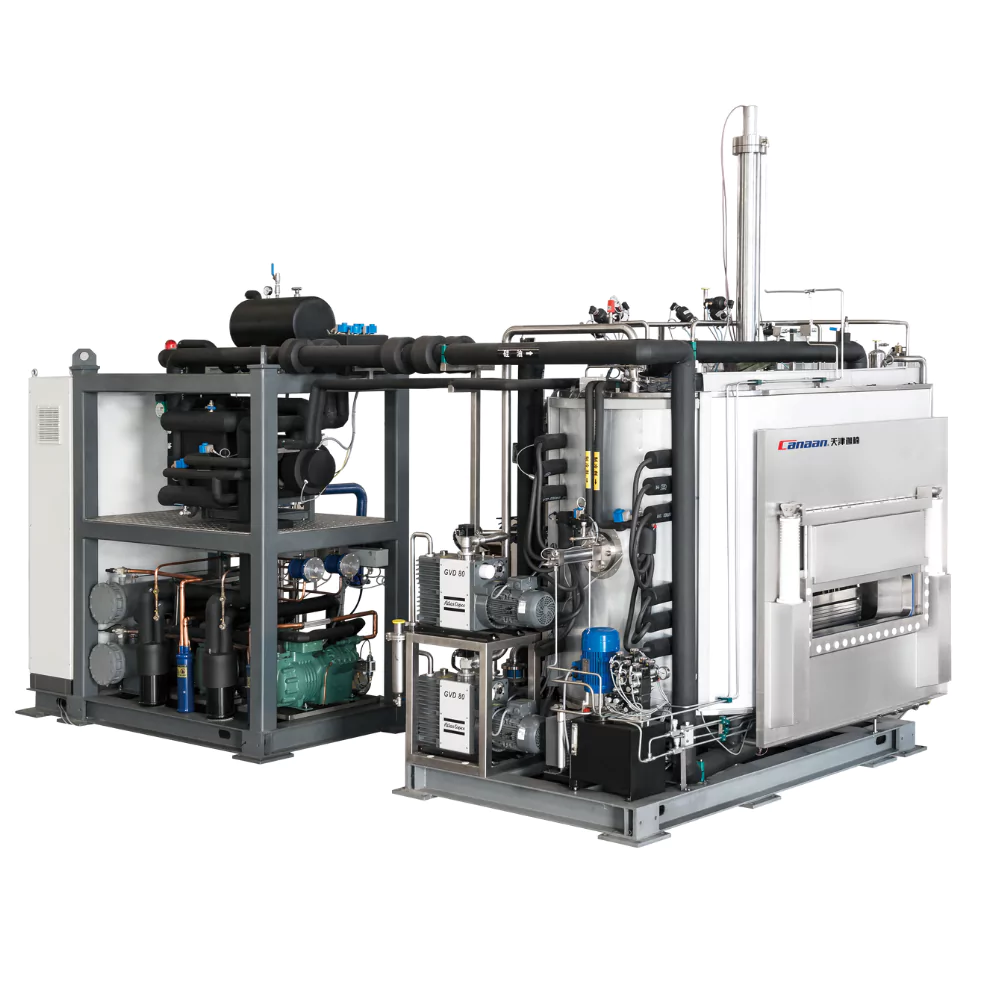

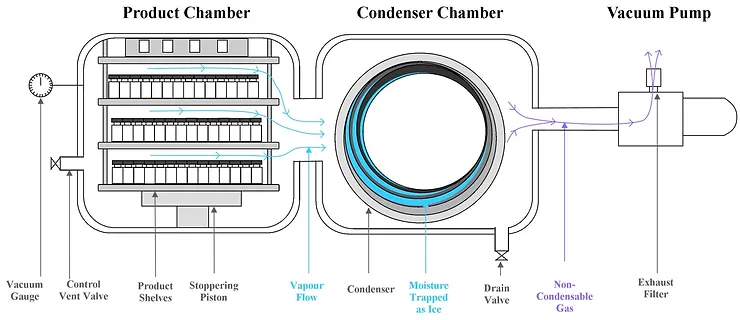

What is lyophilization? Freeze-drying, or lyophilization, is an important process in the pharmaceutical industry. It helps preserve medicines, vaccines, and other sensitive products by removing moisture. If you buy a used freeze-dried machine, it’s essential to take proper care of it. Proper maintenance will extend the machine’s life, improve efficiency, and ensure the safety and […]

What is freeze-drying? Freeze drying, also called lyophilization, is a method used to preserve medicines, vaccines, and other sensitive products. It removes moisture from products, which helps them stay stable for longer. In the pharmaceutical industry, freeze-drying is key to storing important products, like biologics and vaccines, without needing refrigeration. For freeze-drying to work, you […]

In the pharmaceutical industry, two common methods for drying products are freeze-drying and spray-drying. These methods remove water from products like medicines and vaccines, making them last longer and easier to store. But how do they work? And which one is better for different types of products? Let’s explore the differences between freeze-drying and spray-drying, […]