Pharmaceutical coatings are a fundamental part of drug development and manufacturing, offering multiple advantages such as protection, taste masking, and controlled drug release.
These coatings help ensure that medications are not only effective but also patient-friendly. The coating process involves applying a thin layer of a protective substance over the surface of tablets, capsules, or granules.
Pharmaceutical coatings not only enhance the drug’s appearance but also improve its stability and performance.
In this article, we’ll explore the concept of pharmaceutical coating, and dive deep into the different types: sugar coating, film coating, and enteric coating.


Ready To Take Your Production to the Next Level with a High-Performance Coating Machine?

What is pharmaceutical coating? Pharmaceutical coating is the process of applying a thin film of material to a solid dosage form. These coatings are typically polymers or sugar-based solutions that serve various purposes depending on their formulation.
The coatings can be protective, functional, or decorative. Whether it’s masking an unpleasant taste, controlling the rate of drug release, or protecting sensitive ingredients from environmental factors, pharmaceutical coatings are vital for enhancing both drug efficacy and patient compliance.
The choice of coating depends on several factors, including the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API), the drug’s required release profile, and the manufacturing process itself.
Coatings also play a key role in meeting the regulatory requirements for drug safety and efficacy. As drug delivery systems evolve, so too does the complexity and capability of pharmaceutical coatings.
Now, let’s look at the main types of coating commonly used in the industry.
What are the different types of coating? The different types of coating are sugar coating, film coating, and enteric coating.
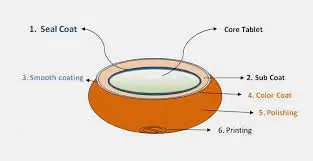
What is sugar coating? Sugar coating is one of the oldest and most traditional methods used in pharmaceutical manufacturing. This process involves the application of several layers of sugar-based syrups to the tablet’s surface.
These layers are applied in multiple stages, each serving a different function—starting from sealing the core of the tablet to applying a smooth and shiny final layer. The result is a glossy, polished tablet with a sugar-based outer layer.
Sugar coating is particularly suited for masking the unpleasant taste or odor of certain medications. By covering the tablet in a sugar layer, the process significantly improves the palatability of the drug, especially for children. This coating method also adds aesthetic value to the tablets, making them more visually appealing and easier to differentiate.
The downside, however, is that sugar coating increases the size and weight of the tablet. As a result, this method is less suited for modern formulations where tablet size must be kept small for ease of swallowing.
The process itself is also labor-intensive and time-consuming, requiring multiple layers to achieve the final product. For these reasons, sugar coating has largely been replaced by more efficient techniques like film coating.
Despite these limitations, sugar coating is still used today in cases where taste masking is crucial, and the additional size of the tablet is not a significant issue.
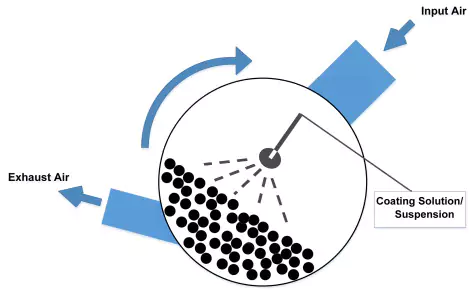
What is film coating? Film coating is the most widely used pharmaceutical coating method today.
Unlike sugar coating, film coating involves the application of a thin layer of polymer-based film onto the surface of the tablet. This polymer film is usually applied in a single layer using a spray mechanism while the tablets are rotating in a pan. The process is faster and more efficient than sugar coating, and the resulting film is much thinner and more durable.
Film coating offers several advantages, including protection against environmental factors, improved aesthetics, and the ability to modify the drug release profile. The film coating can be transparent or colored, depending on the desired appearance of the tablet.
One of the biggest advantages of film coating is that it does not significantly increase the size of the tablet, making it ideal for patients who struggle with swallowing large tablets. Film-coated tablets are also more durable and less likely to break or chip during handling or transportation.
The film coating process typically involves three steps:
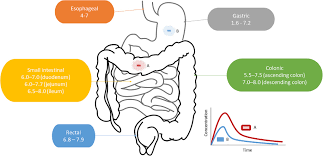
What is enteric coating? Enteric coating is a specialized type of film coating designed to resist the acidic environment of the stomach. This coating allows the tablet to pass through the stomach intact and dissolve in the more neutral pH environment of the small intestine.
Enteric coatings are often applied to drugs that can cause irritation to the stomach lining or that are unstable in acidic conditions.
The materials used for enteric coatings are pH-sensitive polymers that only dissolve at a higher pH, ensuring that the drug is released in the intestine rather than the stomach.
Suitability – Enteric coating is suitable for drugs that:
Advantages of Enteric Coating:
However, the complexity of enteric coating means that it can be more expensive and time-consuming to produce compared to other coating methods.

We’ve Provided Detailed Comparisons to Help You Make an Informed Decision. Below are In-depth Comparisons of the Three Different Coating Types.
Choosing the right pharmaceutical coating method can greatly impact the success of your drug formulation and its acceptance by patients. Whether you’re looking to mask unpleasant tastes with sugar coating, protect and enhance the function of your drug with film coating, or ensure the proper release of your drug in the digestive system with enteric coating, having the right equipment and expertise is essential.
At China Canaan, we provide a range of advanced coating machines tailored to meet your production needs. Our machines offer precision, efficiency, and uniformity, ensuring that each tablet or capsule is perfectly coated every time.
Contact us today to explore our solutions and enhance your pharmaceutical production line.




Before any drug reaches a patient, it starts in a lab. That’s where formulas are tested, batches are checked, and quality is either confirmed or questioned. To do that work right, labs depend on the right equipment—tools that don’t just get the job done, but do it with precision. If you’re responsible for running or […]

Blister packaging is everywhere in pharma—from tablets to capsules to sample packs. It protects the product, extends shelf life, and improves patient safety. But for manufacturers, it’s more than just packaging—it’s a system built around speed, precision, and compliance. If you’re in pharma manufacturing or packaging procurement, here’s what you need to know about blister […]

If you’re deciding how to deliver a pharmaceutical or supplement product, the format you choose—liquid gels or tablets—will shape more than just how it looks. It affects how the product is made, how fast it’s absorbed, what kind of equipment you’ll need, and how the end user experiences it. Some actives work better in a […]