In pharmaceutical manufacturing, granulation is a crucial step to convert fine powders into free-flowing granules, which are then used to produce solid dosage forms such as tablets or capsules.
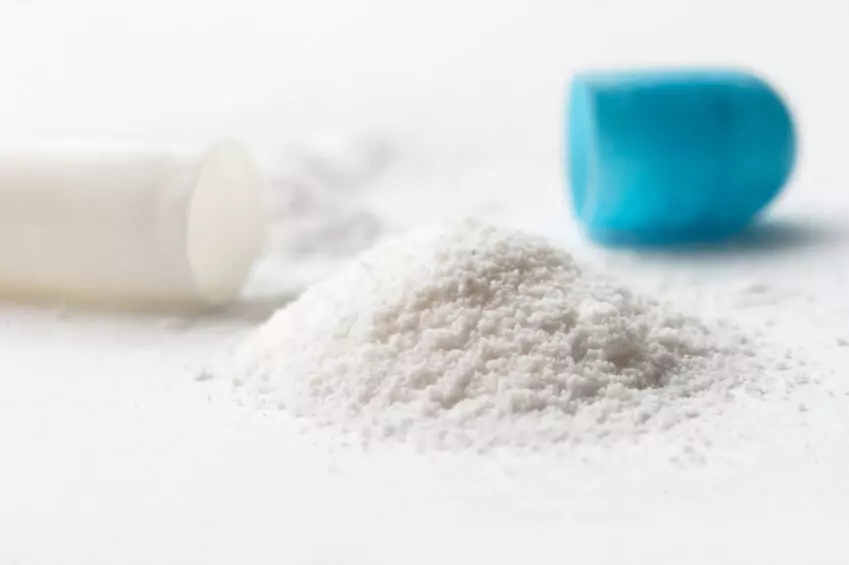

Granules are preferred because they have better flow properties and compressibility, which helps ensure uniformity in dosage and tablet weight. One of the most effective methods for dry granulation is roller compaction.
What is roller compaction? Roller compaction compresses powders between two rotating rollers to form solid ribbons or sheets. These ribbons are then milled into granules without the use of water or solvents, making this method ideal for heat-sensitive and moisture-sensitive active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs).

Roller compaction is efficient, cost-effective, and scalable, making it widely used in large-scale pharmaceutical production.
| Step | Description |
| Powder Feeding | Feed the powder blend steadily into the roller compactor. |
| Compaction | Compress the powder between rollers to form dense ribbons. |
| Granulation | Break down the ribbons into smaller, free-flowing granules for further use. |
The granulation process in a roller compactor involves three key steps:
The entire roller compactor granulation process is efficient and repeatable, which makes it well-suited for large-scale pharmaceutical production.
| Parameter | Influence on Granulation |
| Roller Pressure | Higher pressure increases density; too high can cause degradation. |
| Roller Speed | Affects ribbon thickness; slower speeds yield thicker ribbons. |
| Feeding Rate | Consistent feeding ensures uniform granules; fluctuations cause variation. |
| Roller Gap | Smaller gap creates thinner ribbons; larger gap makes thicker ribbons. |
| Powder Properties | Particle size, moisture, and flowability affect compaction quality. |
Several critical parameters influence the quality of the granules produced by roller compaction:
Careful control of these parameters is essential to produce granules with the desired characteristics, such as flowability, compressibility, and uniform particle size distribution. Manufacturers often rely on advanced control systems and real-time monitoring to ensure consistency and product quality during roller compaction.
Looking to enhance your pharmaceutical manufacturing process with advanced roller compaction technology?
At China Canaan, we offer state-of-the-art roller compaction systems designed for precision, efficiency, and scalability. Our machines feature advanced control systems that allow for real-time monitoring of critical parameters, ensuring consistent granule quality every time.
Whether you are working with moisture-sensitive APIs or require high-throughput production capabilities, we have the solution to meet your needs. Our roller compactors are engineered for high-performance, continuous operation, and are customizable to suit a wide range of pharmaceutical applications.



Contact us today to learn how we can help optimize your granulation process and improve your production efficiency.





Manufacturing pharmaceutical products should always be taken seriously. That is, every process must follow the strictest and highest standards. This is the very reason why manufacturers prefer hiring an EPC contractor. Contractors working under EPC contracts will ensure the outcomes are of the best quality no matter what happens, focusing on the construction of the […]

Explore the importance of EPC contracts in pharmaceutical manufacturing. Learn how EPC works, its benefits, and why choosing an EPC contractor can guarantee project success with Canaan’s industry-leading equipment.

Discover how SCADA and PLC improve automation in the pharmaceutical industry. Learn their roles, benefits, and how Canaan’s advanced technology enhances efficiency and safety.