In pharmaceutical manufacturing, the production of solid dosage forms—such as tablets and capsules—relies on precise processes to ensure consistent quality and efficacy.
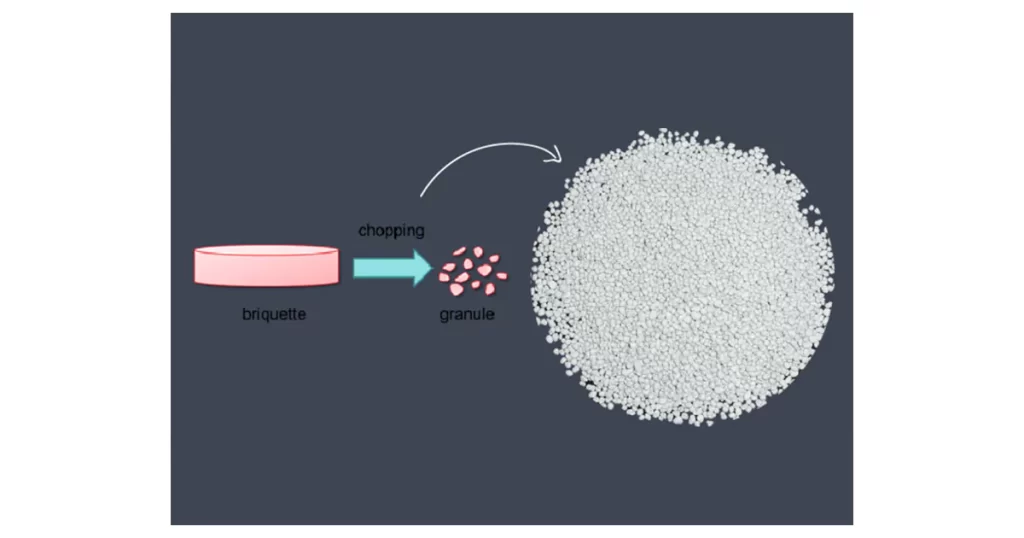
A crucial part of this process is granulation, where fine powders are transformed into granules that are easier to handle and compress into uniform tablets. Granulation improves the flowability and compressibility of powders, which is essential for producing high-quality tablets with uniform dosages.
There are two main methods of granulation: wet granulation and dry granulation.
Wet granulation uses liquids to bind powders, but this method isn’t suitable for all materials, especially those sensitive to moisture or heat. In such cases, dry granulation becomes the preferred method, with roller compaction being one of the most widely used techniques.
Roller compactors are critical tools in the pharmaceutical industry, providing a dry granulation method that eliminates the need for solvents. This method is particularly important when dealing with active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) that are sensitive to moisture or heat, as it prevents degradation and ensures product stability.
Pharmaceutical companies use roller compactors to compress powders into dense ribbons or sheets, which are then milled into uniform granules. These granules are later used to produce tablets or filled into capsules. This process offers several advantages over wet granulation, including improved product stability, faster processing times, and reduced energy consumption.
What is a roller compactor? A roller compactor is a piece of machinery that uses mechanical force to compact powders into solid ribbons or sheets, which are then milled into uniform granules.
This method is particularly important when dealing with active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) that are sensitive to moisture or heat, as it prevents degradation and ensures product stability.
Pharmaceutical companies use roller compactors to compress powders into dense ribbons or sheets, which are then milled into uniform granules. These granules are later used to produce tablets or filled into capsules. This process offers several advantages over wet granulation, including improved product stability, faster processing times, and reduced energy consumption.
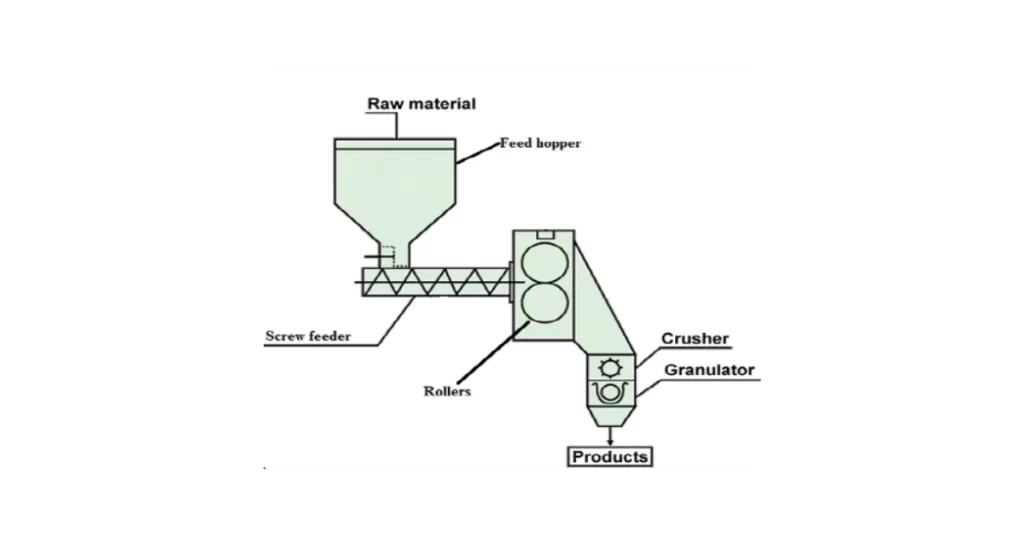
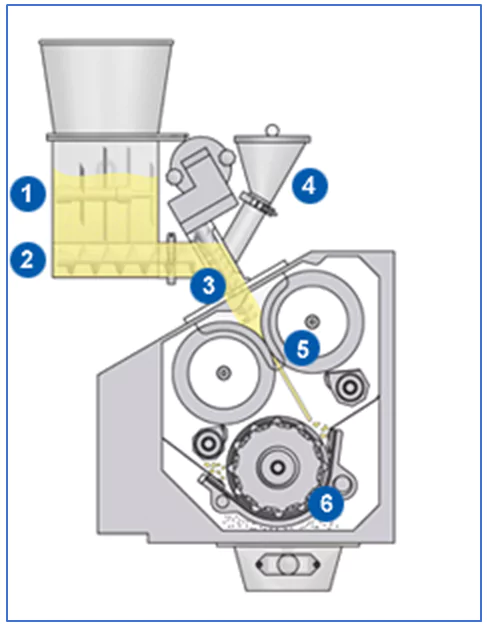
The feeding system consists of a hopper and auger feeder that transfers the powder blend into the compaction area. The consistency of feeding is crucial, as it affects the quality and uniformity of the granules.
The compaction unit is where the magic happens. Two counter-rotating rollers apply mechanical pressure to compress the powder into dense ribbons or sheets. The pressure, roller speed, and gap between the rollers are carefully controlled to achieve the desired granule density and size.
Once the ribbons are formed, they are fed into the size reduction unit (granulator), where they are broken down into granules. The granule size can be adjusted by changing the settings on the granulator, allowing for precise control over particle size distribution.
| Advantage | Description |
| No Need for Solvents | Eliminates moisture/heat risks; no drying stage required. |
| Improved Granule Density | Enhances flowability; facilitates uniform tablet compression. |
| Reduced Processing Time | Lowers production costs and increases throughput. |
| Scalability | Easily transitions from lab to full-scale production. |
| Continuous Processing | Enables uninterrupted granulation, reducing downtime. |
| Consistent Granule Quality | Controls density and particle size for accurate dosages. |
Roller compaction is a dry granulation method, which eliminates the need for water or solvents. This is particularly advantageous when working with APIs that are sensitive to moisture or heat. Since no liquids are involved, there is no need for a drying stage, which simplifies the process and reduces energy consumption.
Roller compaction increases the bulk density of powders, improving their flowability and making them easier to compress into uniform tablets. This is especially important for high-speed manufacturing lines where consistent powder flow is critical to maintaining efficiency.
Without the need for wetting or drying steps, roller compaction reduces overall processing time. This results in lower production costs and increased throughput, making it an attractive option for large-scale pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Roller compaction can be scaled easily from laboratory-scale experiments to full-scale production. This scalability allows manufacturers to optimize their processes before scaling up, ensuring consistent quality across batches.
Roller compactors support continuous processing, meaning that materials can be fed into the machine and granulated without interruption. This increases efficiency and reduces downtime, making it suitable for high-volume production environments.
By precisely controlling compaction force and roller speed, manufacturers can produce granules with uniform density and particle size distribution. This consistency is crucial for ensuring that every tablet or capsule contains the correct dosage of the active ingredient.
| Trend | Description |
|---|---|
| Integration of Process Analytical Technology (PAT) | Real-time monitoring of critical parameters (e.g., compaction force, roller speed) to ensure product quality and reduce waste. |
| Enhanced Automation and Control Systems | Advanced control systems for automatic monitoring and adjustments, reducing human error and increasing efficiency. |
| Containment for High-Potency Compounds | Equipment designed with enhanced containment features to protect operators from exposure to hazardous substances. |
| Sustainability and Energy Efficiency | Focus on reducing energy consumption and eliminating solvents, contributing to greener manufacturing practices. |
| Continuous Manufacturing | Shift towards continuous processing to improve efficiency and reduce costs, making roller compactors integral to modern manufacturing lines. |
The future of roller compaction in pharmaceuticals is being shaped by advancements in technology and manufacturing processes. Several key trends are emerging:
PAT allows real-time monitoring of critical process parameters, such as compaction force, roller speed, and ribbon density. By integrating PAT, manufacturers can make adjustments during the process to ensure consistent product quality and reduce waste.
Automation is playing an increasingly important role in pharmaceutical manufacturing. Modern roller compactors are equipped with advanced control systems that allow operators to monitor and adjust key parameters automatically, reducing the risk of human error and increasing efficiency.
As the demand for high-potency APIs increases, roller compaction equipment is being designed with enhanced containment features to protect operators from exposure to hazardous substances. This is particularly important when working with compounds that have low occupational exposure limits (OELs).
Sustainability is becoming a priority in pharmaceutical manufacturing, and roller compaction is contributing to this trend by reducing energy consumption and eliminating the need for solvents. As more manufacturers adopt green practices, roller compaction will continue to play a role in sustainable pharmaceutical production.
The pharmaceutical industry is moving toward continuous manufacturing to improve efficiency and reduce costs. Roller compactors are well-suited to continuous processing, making them an integral part of modern manufacturing lines. As continuous manufacturing becomes more widespread, roller compactors will play a key role in ensuring consistent product quality.
China Canaan stands out as a leading manufacturer of roller compactors, offering innovative solutions for pharmaceutical dry granulation. Here’s why:
Looking for high-performance roller compaction equipment?
Contact us today to learn more about how we can support your pharmaceutical manufacturing needs with state-of-the-art solutions.




Manufacturing pharmaceutical products should always be taken seriously. That is, every process must follow the strictest and highest standards. This is the very reason why manufacturers prefer hiring an EPC contractor. Contractors working under EPC contracts will ensure the outcomes are of the best quality no matter what happens, focusing on the construction of the […]

Explore the importance of EPC contracts in pharmaceutical manufacturing. Learn how EPC works, its benefits, and why choosing an EPC contractor can guarantee project success with Canaan’s industry-leading equipment.

Discover how SCADA and PLC improve automation in the pharmaceutical industry. Learn their roles, benefits, and how Canaan’s advanced technology enhances efficiency and safety.